Documentation
Run Page
1 - First Oligomeric form
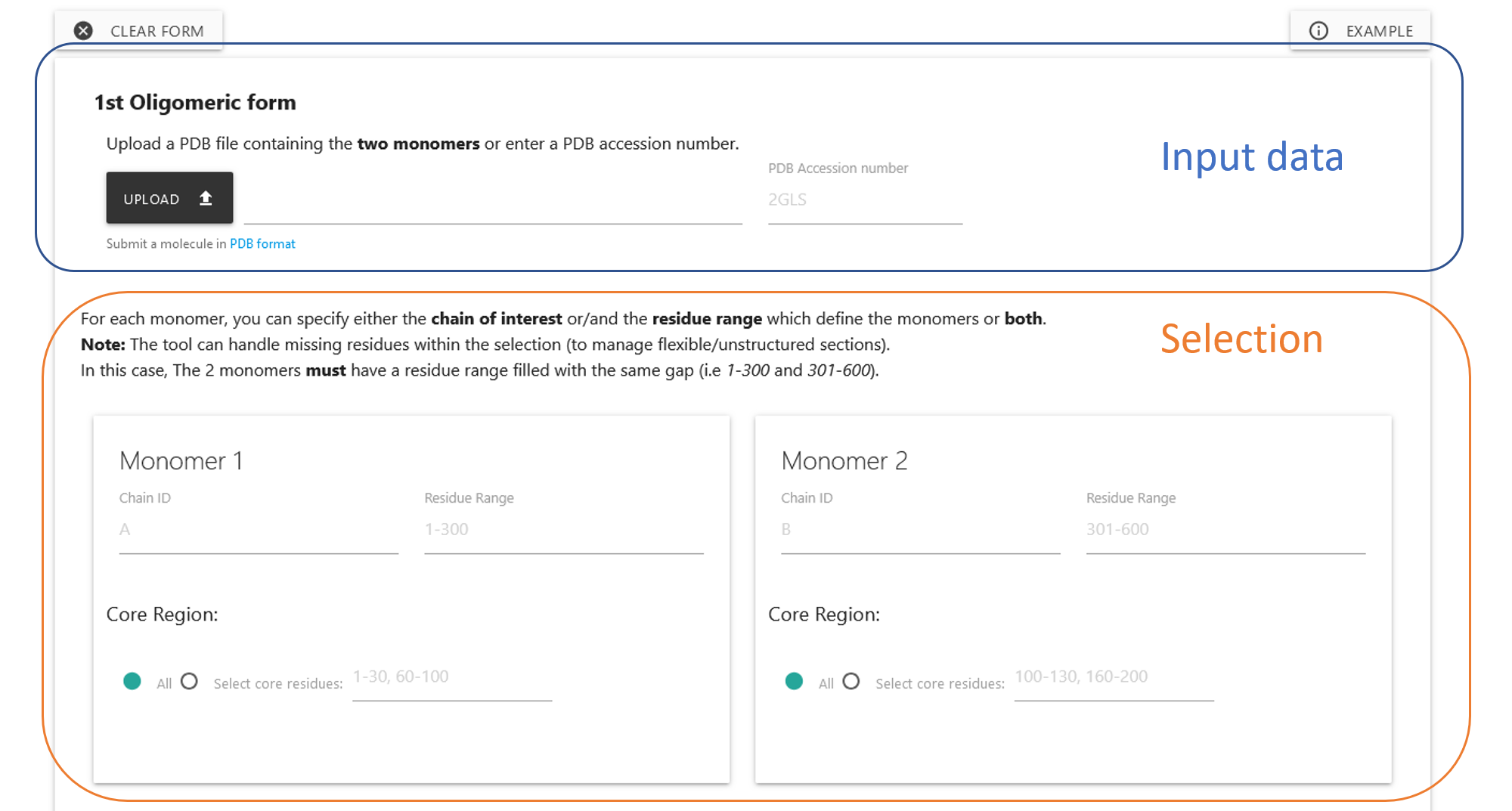
The input form is organised in two parts: the Input data
and the Selection.
In the Input data, you can either:
- choose an input file. Only the PDB format is accepted.
- select a PDB id taken from https://www.rcsb.org/
Note: A cleaning step is performed in which all HETATM and water atoms are discarded from the input PDB.
Each monomer may be specified by the chain, the residue range, or both and this definition dictates what will be includd in the displayed molecule and any constructions.
priority_highOnly the α-Carbons of the monomers will be used for computing the helical parameters; both monomers need to have the same number.priority_high
Core Region: If specified, a core region is a region of the specified monomer which will be used to compute the helical parameters and the residues at the interface. This may be necessary to focus the helical analysis on structurally similar (low-rmsd) "core" regions of the two specified monomers.
priority_highCareful! Even if a core is defined, during the construction of an oligomer the whole monomer defined by the chain/residue range will be used, not just the core region.priority_high
Missing Residues
Heligeom can handle missing residues in one monomer compared to the other:
- if only the chain is provided, any missing residues inside that chain are handled.
- if residue ranges are provided: any missing residues at the beginning or end are also handled assuming the same residue numbering difference applies throughout the ranges. For example, if residue ranges 1-300 and 301-600 are specified, then all residues in each monomer having a residue id difference of 300 will be retained for the helical parameter analysis.
Non-protein atoms
As stated above, all HETATM and water atoms are discarded from the input before the selection process.
If one wishes to keep non-protein atoms for the oligomer construction step, we suggest renaming the corresponding atom lines in the PDB file from "HETATM" to "ATOM ". They will not be used for the Screw calculation because only α-Carbon monomers are handled.
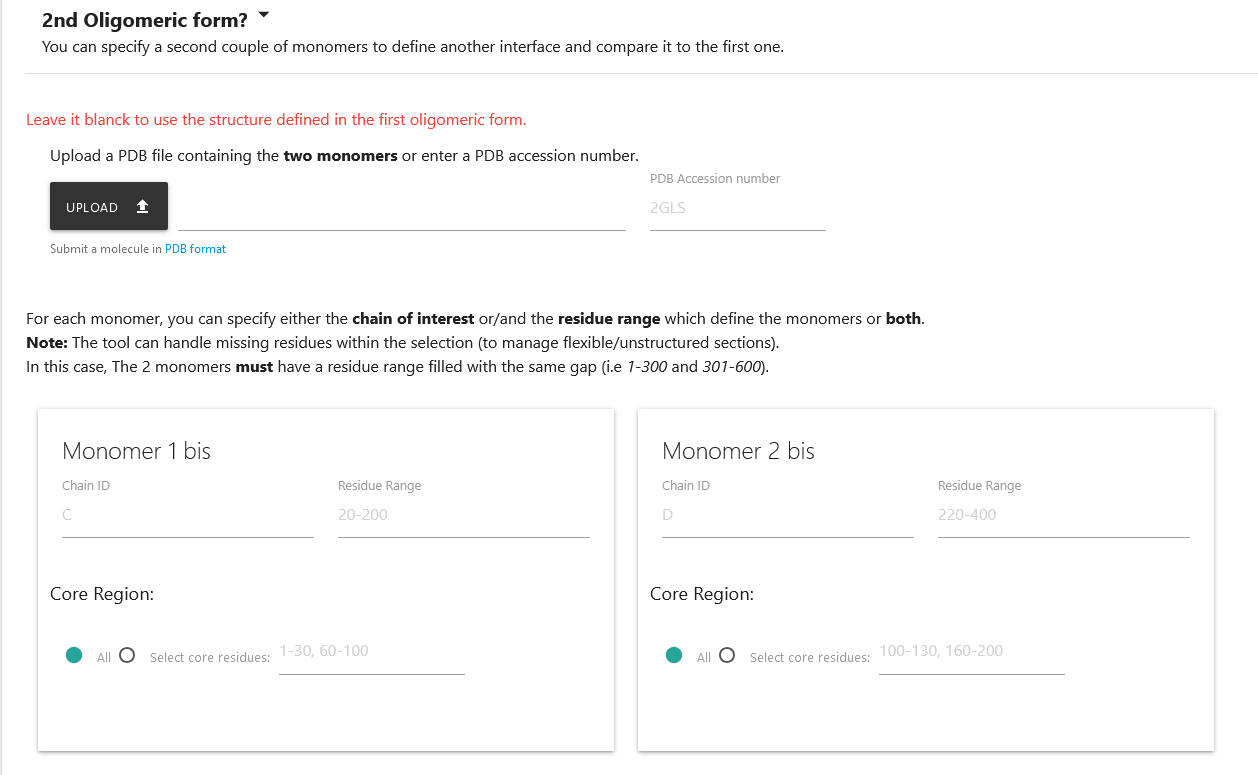
2 - 2nd Oligomeric form (Optional)
Helligeom allows you also to compare 2 interfaces by specifying a second interface.
To do so, you must click on the text 2nd oligomeric form?, and a new input form as for the first oligomeric form will appear.
3 - Run
Clicking on the Analyze button starts the computation. The Results page is displayed once the calculation is complete.

Results Page with 1 Oligomer
Contacts at the interface

On the left, Heligeom displays a summary of the input parameters.
For each monomer, you will see the specified chains, the residues ranges, and the core regions.
If any field is not specified, the word "Unspecified" is displayed instead.
On the right, there is a Mol* visualisation depicting:
- the two monomers selected by the user represented as Cartoon and whose colors match their respective titles on the left.
- the residues in contact at the interface, represented as ball and stick
List of contacts: The list of contacts can be downloaded by clicking Download list of contacts.
A contact is defined when 2 heavy atoms, one from each monomer, are at a distance < 5Å.
Helical parameters

Heligeom displays the helical parameters computed from the 2 provided monomers.
It refers to the screw calculation.
priority_highThis calculation is based solely on the α-Carbons of the monomers.priority_high
- The pitch is the distance of one helix turn along the helix axis.
- The monomers per turn is the number of monomers needed for 1 turn of the helix.
- The Handedness is the direction of rotation around the axis.
- The 2 distances (IntR and ExtR) are the minimal and maximal distances between the screw axis and the atoms of the oligomer.
On the right:
- The parameters of the Screw axis are provided along with a schematic of the parameter definitions. The parameters will be used to construct the oligomer in the next step.

RMSD: The RMSD value of the α-Carbon superposition of the two monomers is displayed.
Heligeom uses color to provides a hint for interpreting this value depending on the value:
- RMSD <= 2Å: The RMSD of the superposition is acceptable.
- 2 < RMSD <= 5Å: The construction of the oligomer could be incorrect.
- RMSD > 5Å: The construction of the oligomer will lead to incorrect results.
Construction Details
Once the helical parameters are computed, Heligeom can construct an oligomer based on them.
The protocol is
- take the entire Monomer 1 selection (not just the core regions), including non-protein atoms if they are part of the selection.
- create copies of this monomer applying the screw transformation
- repeat the above step to match the number of monomers provided as input.
Write a mmCIF file?: This option writes the structure file for the oligomer using the mmCIF file format instead of the PDB flat-file format. This is useful when constructing assemblies with more than 62 chains.
Flatten the oligomer?
The method is described in the About page.
This computation can take up to several minutes due to the underlying Monte-Carlo calculation.
Once finished, below the visualisation section, Heligeom displays several parameters resulting from the calculation.
Once the construction is finished, an interactive view of the oligomer is displayed below the input form (thanks to Mol*).
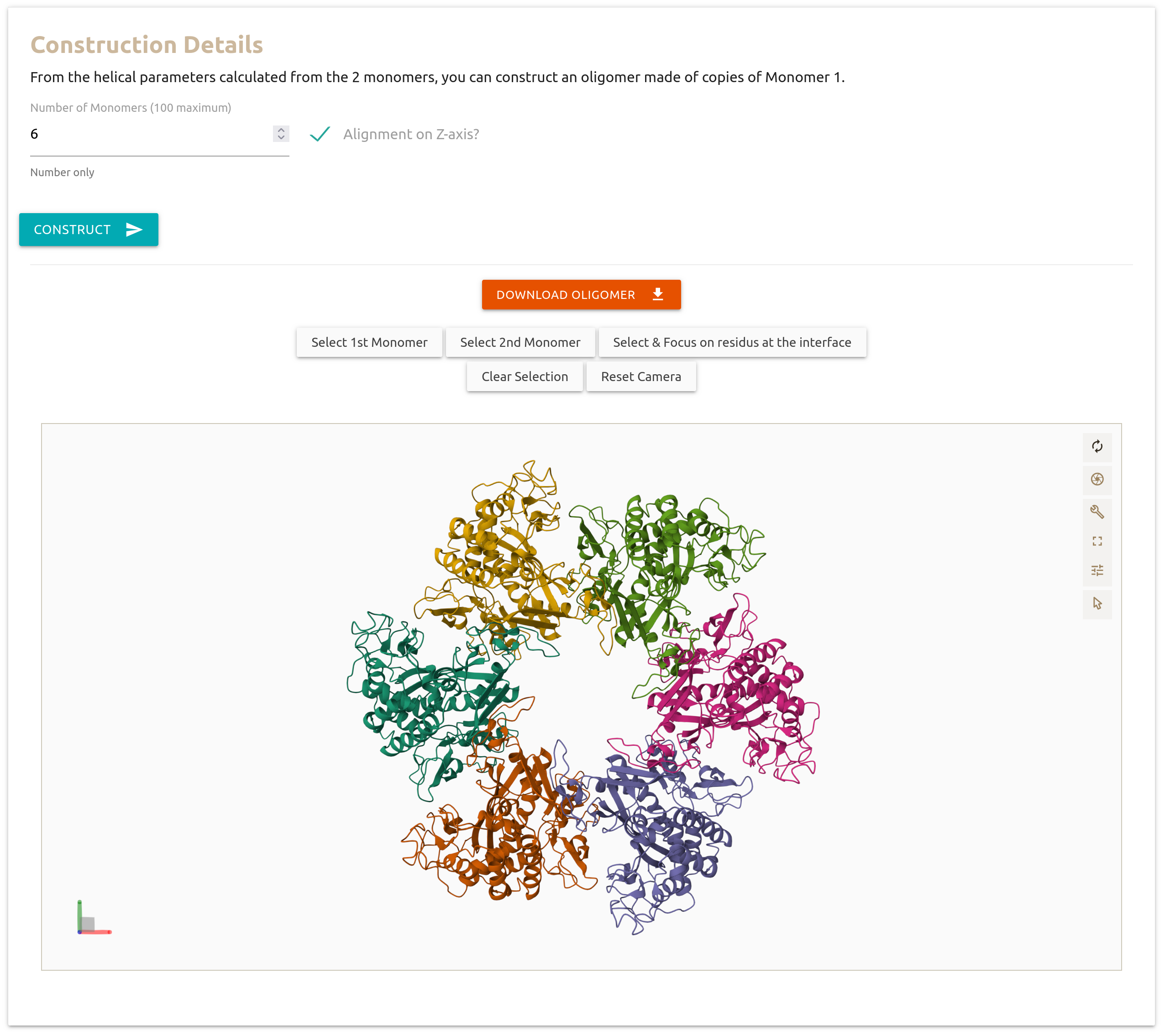
By default, the coloring is by monomer. Each monomer will have a different chain, starting by A.
A set of precomputed visualization buttons is available above the view.
You can download the PDB file of the generated oligomer to your computer by clicking on the orange button.
Result Page with 2 oligomeric forms
Results

For two oligomeric forms, Heligeom displays the same content that for 1 Oligomer with a side-by-side view.
Comparison of the interfaces

On the Results page, Heligeom displays some analyses comparing the 2 interfaces.
fNAT
The fNAT is the fraction of residue contact pairs of the 1st interface present in the 2nd interface, as defined
here.
Value of 1.0: All of the contacting residue pairs of the 1st interface are present in the 2nd one.
Value of 0.0: None of the contacting residue pairs of the 1st interface are present in the 2nd one.